3M
3M offers innovative solutions to the electronics industry and is a leading manufacturer of interconnect solutions for board-to-board, wire-to-board, backplane and input/output (I/O) applications. These include 3M™ Wiremount Insulation Displacement Contact (IDC) Connectors, Mini Delta Ribbon (MDR) I/O System, Mini-Clamp Discrete Wire System, MetPak™ High Speed Hard Metric (HSHM) and the new Ultra Hard Metric (UHM) Backplane Connectors. Using industry leading capabilities in CAD - such as NX™ and SLA modeling - 3M's experienced engineers turn ideas into real world solutions.3M offers solutions for printed circuit board fabrication, board assembly and test, such as adhesives and tapes, embedded capacitor materials, Textool™ Test and Burn-in Sockets, carrier and cover tapes and trays, flexible circuits, and products for reducing electrostatic discharge. 3M also offers solutions for shielding from EMI/RFI, for thermal management and vibration damping, as well as for packaging and labeling.
3M
Extremely fast response to your needs
Save you time, money, and trouble
Save you time, money, and trouble
We treat each other sincerely, long-term cooperation, Jiquan Electronics only focuses on 3M (3M) Component spot channels
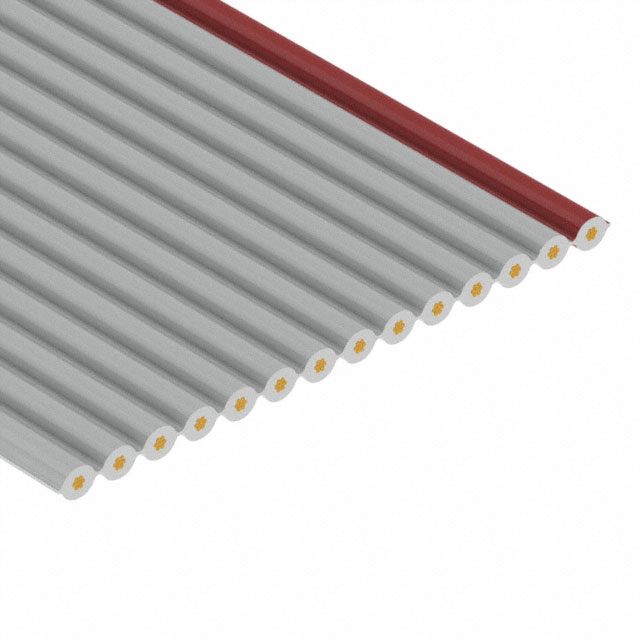
3365/14 300SF
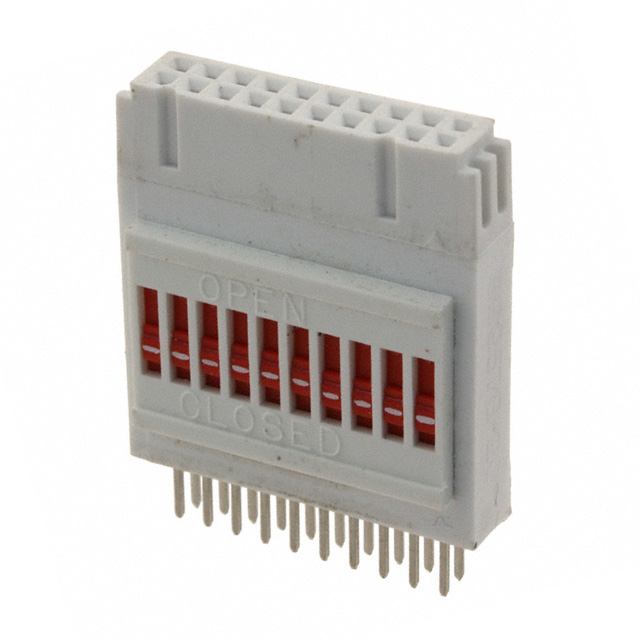
929665-03-36-I
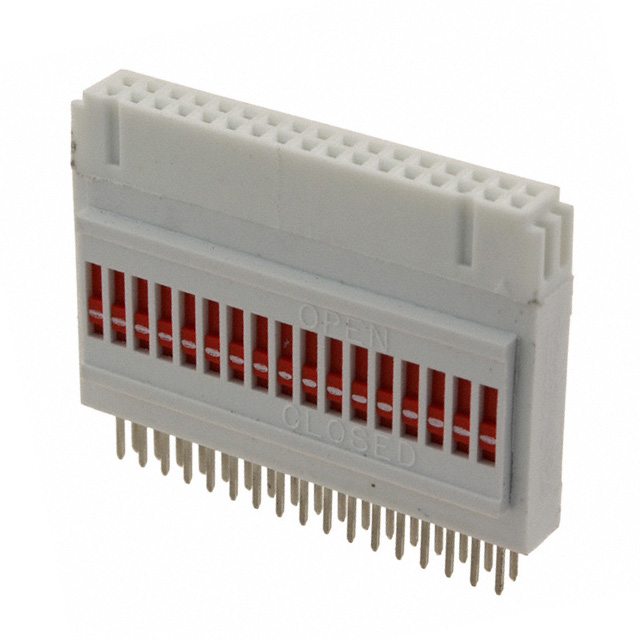
922576-20-I
922576-26-I
922576-34-I
922576-40-I
922576-50-I
922578-20-I
922578-34-I
922578-40-I
922578-50-I
3366-1000
3548-1000
3548-1002
3564-1000
3572-1000
M7LTK-1405K
M7LXK-1410K
M7QXK-5005K
M7RXK-3605K
3302/20 300SF
3302/24 300SF
3302/34 300SF
3302/40 300SF
3302/64 300SF
3365/10 300SF
3365/16 300SF
3365/34 300SF
3365/37 300SF
923830-BK-C
923830-BU-C
923830-GN-C
923830-RD-C
923830-WT-C
923830-YL-C
923835-BK-C
923835-BU-C
923835-GN-C
923835-RD-C
923835-WT-C
923835-YL-C
923840-BK-C
923840-RD-C
923845-RD-C
923848-C
923850-C
929647-02-36-I
929647-03-36-I